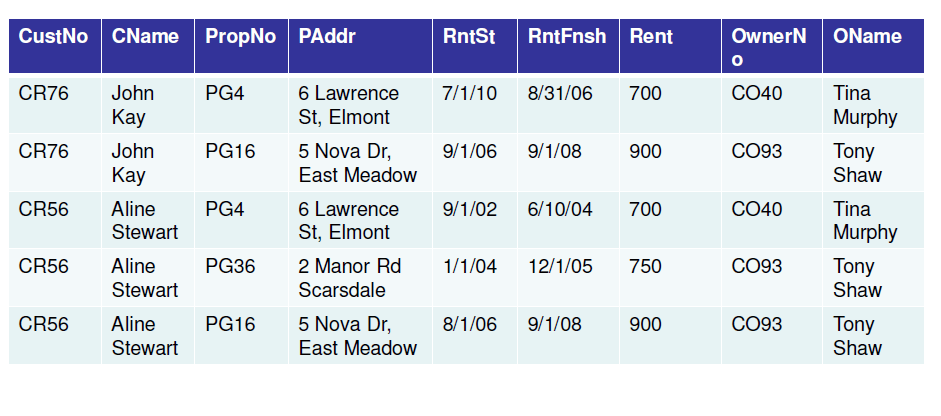
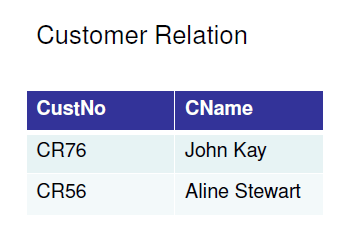
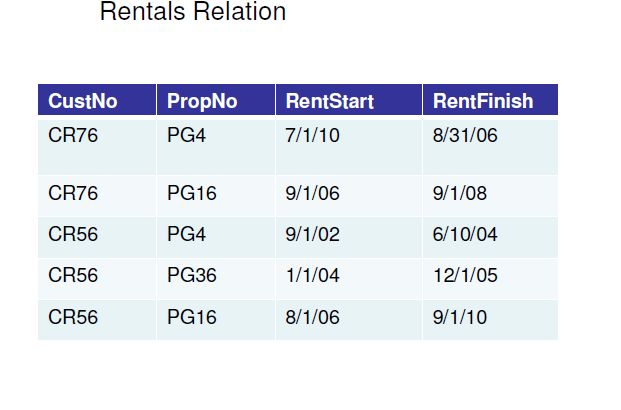
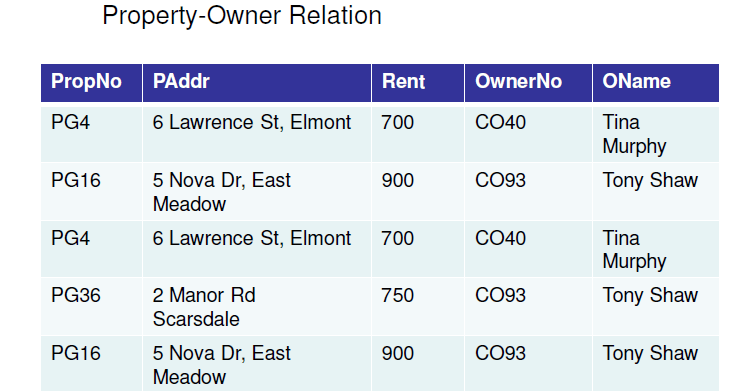
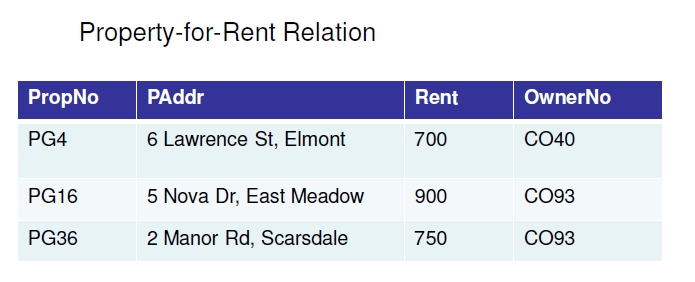
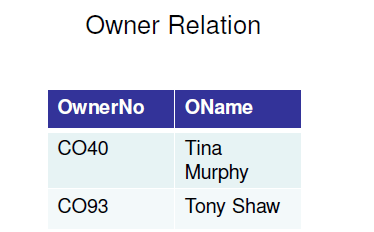
It is essential to have understandings of functional dependencies in normalizing the tables.
“A value X determines value of Y .” or X->Y.
Which means that it is a constraint that Y is determined by the value of X but this is not Vice versa !
It does not necessarily means that Y determines X.
For instance, In USA , every person has a unique social security No ,referred to as SSN , uniquely identifies each person. So , according to the definition , consider X being the SSN and Y being a person name .
Example :
SSN : 11223344 is assigned to the person ABC . This satisfies the functional dependency SSN -> personName
But vice versa is not necessary that it fulfills the condition . There can be hundreds or thousands of Mr ABC in the USA ! so vice versa cannot satisfy the condition.
Remember the following functional dependency Rules :
- Reflexivity : If Y is subset of X , then X determines Y that is X->Y.
For example : Consider {EmpID,EmpName} -> EmpID , this satisfies the rule of reflexivity because EmpID is a subset of {EmpID,EmpName} .
2. Augmentation : If X-> Y , then XZ->YZ .
For example : Consider EmplD being X , EmpName being Y and Z being EmpBirthDate . EmpID -> EmpName , so {EmpID, EmpBirthDate} -> {EmpName , EmpBirthDate} .
3. Transitive : If X -> Y and Y -> Z is true, then X-> Z is a transitive dependency.
MovieID, ListID, Genre and Price.
MovieID-> ListID
ListID-> Genre
4. Decomposition : {X→YZ} |=X→Y.
If a table has two columns which are determined by the same primary key then break them up into two different tables.
5. Union : {X→Y, X→Z} |=X→YZ .
Which means that if X determines Y and X determines Z then Y and Z can be put together in a table depending on the situation because they can be determined by same Primary Key X.
6. Pseudotransitive : If X-> Y and YW->Z ,then XW->Z .
Thank You