Here is an example of inserting into a temporary table from multiple joins:
select a.col,b.col,c.col into #temp1
from table1 a
join table2 b on a.column1ID= b.column2ID
join table3 c on a.column1ID= c.column3ID
where c.col= ‘anydata’
Author: Ahmed Mujtaba
Here is an example of inserting into a temporary table from multiple joins:
select a.col,b.col,c.col into #temp1
from table1 a
join table2 b on a.column1ID= b.column2ID
join table3 c on a.column1ID= c.column3ID
where c.col= ‘anydata’
Today while connecting my MS SQL 2012 Server after a long time , i came across an error :
A network-related or instance-specific error occurred while establishing a connectionto SQL Server. The server was not found or was not accessible. Verify that the instance name is correct and that SQL Server is configured to allow remote connections.(provider: Named Pipes Provider, error: 40 – Could not open a connection to SQL Server) (Microsoft SQL Server, Error: 2)
I checked services of my pc , by typing the “services.msc” in the run , which opens the services dialog box .Then started the services of SQL Server which were not in running state.
I was then able to connect
Best Regards,
OVERVIEW :
USE msdb
Go
SELECT j.name JobName,h.step_name StepName,
CONVERT(CHAR(10), CAST(STR(h.run_date,8, 0) AS dateTIME), 111) RunDate,
STUFF(STUFF(RIGHT(‘000000′ + CAST ( h.run_time AS VARCHAR(6 ) ) ,6),5,0,’:’),3,0,’:’) RunTime,
h.run_duration StepDuration,
case h.run_status when 0 then ‘failed’
when 1 then ‘Succeded’
when 2 then ‘Retry’
when 3 then ‘Cancelled’
when 4 then ‘In Progress’
end as ExecutionStatus,
h.message MessageGenerated,*
FROM sysjobhistory h inner join sysjobs j
ON j.job_id = h.job_id
where j.name =’jobname’
ORDER BY j.name, h.run_date, h.run_time
GO
There is a difference between union and a union All operator which users are not aware of:
The union all operator will result in a set which will not eliminate the duplicates from the resulting set , means it will return the duplicate rows if residing in the set .
On the other hand union operator will eliminate the duplicates from the resulting set .
Whenever , you see a ALL keyword with union or intersect or except operators , it means it will give all the results including the duplicate records in the set .
To check the number of SQL Servers installed on a LAN or network , we can use the following Commands on your commandline(cmd) :
Also , we can run the following command on Powershell to check the SQL Servers installed on a network with detailed results :
[System.Data.Sql.SqlDataSourceEnumerator]::Instance.GetDataSources()
Tables are the database structures where your data actually gets stored.
Now , we shall create a database table ,you can write the create table below script to create :
use mydatabase; –assuming this is the name of your database
CREATE TABLE dbo.Student — dbo is schema & student is table name
(
studentid INT NOT NULL,
firstname VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
lastname VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
admissiondate DATE NOT NULL,
phoneNumber VARCHAR(18) NOT NULL,
TeacherId INT NULL
);
Named PIPES:
Named Pipes Provider, error: 40 – Could not open a connection to SQL Server
Users / developers often come across this type of errors while connecting /opening MS SQL Server. Here is quick review of how to overcome this issue.
To connect to MS SQL Server , we need network protocols , which connect and communicate with SQL. There are normally four Network Protocols to communicate to MS SQL .
To overcome the above error of Named Pipes , Follow the instructions below :

People face many connectivity issues while connecting to different SQL versions (MS SQL 2005,2008,2012). We shall be providing quick review of how to connect to different Versions on your local machine.
1- Connecting SQL 2005 :
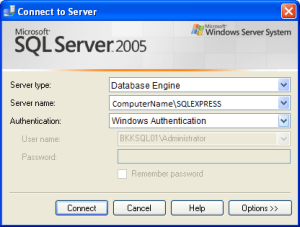
ServerName: is Your computerName which can be found from your My Computer /This PC ‘s and \SQLEXPRESS .
2- Connecting SQL 2008 :

ServerName: is Your computerName which can be found from your My Computer /This PC ‘s and \SQLEXPRESS .
3- Connecting SQL 2012 :

ServerName: is Just Your ComputerName